
Redistribute Questions 3
Here you will find answers to Redistribute Questions – Part 3
Question 1
Given the accompanying output, which additional command is needed to redistribute IGRP into EIGRP?
| Router eigrp 123 Network 10.10.10.0 No auto-summary ! Router igrp 123 Network 172.16.0.0 Network 172.17.0.0 |
A. Under the router igrp mode add redistribute eigrp 123
B. Under the router eigrp mode add redistribute igrp 123
C. Under the router eigrp mode add redistribute igrp 123 subnets
D. None, EIGRP and IGRP are automatically redistributed in this instance.
Answer: D
Explanation
If IGRP and EIGRP use the same Autonomous System (AS) then redistribution occurs automatically. In this case both IGRP & EIGRP use the same AS 123 so they are automatically redistributed.
If IGRP and EIGRP use different AS numbers then redistribution must be done manually.
Question 2
Study the exhibit carefully. Router R1 is connected to networks 172.16.1.0/26 and 172.16.1.64/27. Based on the partial output in the exhibit, which description is correct?

A. Router R1 should be reconfigured with an ACL instead of an ip prefix-list command.
B. Router R1 will advertise both routes.
C. Router R1 will deny the 172.16.1.0/27 route while permitting the 172.16.1.0/26 route to be advertised.
D. Router R1 will deny the 172.16.1.0/26 route while permitting the 172.16.1.64/27 route to be advertised.
Answer: C
Explanation
Prefix lists are configured with permit or deny keywords to either permit or deny the prefix based on the matching condition. A prefix list consists of an IP address and a bit mask. The IP address can be a classful network, a subnet, or a single host route. The bit mask is entered as a number from 1 to 32.
Prefix lists are configured to match an exact prefix length or a prefix range. The ge and le keywords are used to specify a range of the prefix lengths to match, providing more flexible configuration than can be configured with just the network/length argument. The prefix list is processed using an exact match when neither ge nor le keyword is entered.
Therefore in this case the exact 172.16.1.0/26 network is permitted while other networks are denied.
(Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_3t/ip_route/command/reference/ip2_i2gt.html)
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit. The partial configuration for an OSPF ASBR and an Area 0 ABR is shown. Assume the OSPF configurations throughout the network are operable. Which statement about these configurations is true?

A. The ASBR route-maps are basically useless, because there are no deny prefix-lists.
B. LSA Type 5s will not be received by the ABR from the ASBR.
C. The OSPF backbone will not learn any RFC 1918 addresses.
D. The matched prefix-list addresses will be given a metric of 255, which is essentially unreachable.
Answer: C
Explanation
The ASBR accepts RFC 1918 addresses and set these networks to “tag 255” but when advertising into Area 0, the ABR Area 0 filters out these networks because they match “tag 255” so the OSPF backbone will not learn any RFC 1918 addresses.
Note that if you use an ACL in a route-map deny clause, routes that are permitted by the ACL are not redistributed.
All the networks with “tag 255” are blocked by the clause 10 while all other networks are permitted by the clause 20 of the route-map (if a match command is not present, all routes match the clause).
Note:
RFC 1918 addresses include:
+ Class A: 10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255 (10/8 prefix)
+ Class B: 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255 (172.16/12 prefix)
+ Class C: 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255 (192.168/16 prefix)
Question 4
A network administrator is troubleshooting a redistribution of RIP routes into OSPF. Given the exhibited configuration commands, which statement is true?
| rooter rip network 10.0.0.0 ! router ospf 5 network 172.10.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 0 redistribute rip |
A. Redistributed routes will be tagged as external type 1 (E1) with a metric of 30.
B. Redistributed routes will be tagged as external type 2 (E2) with a metric of 20.
C. Redistributed routes will maintain their original RIP routing metric.
D. Redistributed routes will have a default metric of 0 and will be treated as unreachable and not advertised.
E. Redistributed routes will have a default metric of 0 but will not be treated as reachable and will be advertised.
Answer: B
Explanation
By default, all routes redistributed into OSPF will be tagged as external type 2 (E2) with a metric of 20, except for BGP routes (with a metric of 1).
Note: The cost of a type 2 route is always the external cost, irrespective of the interior cost to reach that route. A type 1 cost is the addition of the external cost and the internal cost used to reach that route.
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit. On the basis of the partial configuration, which two statements are correct? (Choose two)
A. Only routes matching 10.0.1.0/24 will be advertised out Ethernet 0.
B. Only routes 10.0.1.0/24 will be sent out all interfaces.
C. Only routes 10.0.1.0/24 will be allowed in the routing table.
D. Only routes matching 10.0.0.0/8 will be advertised out Ethernet 0.
E. Only routes matching 10.0.0.0/8 will be advertised out interfaces other than Ethernet 0.
F. All routes will be advertised out interfaces other than Ethernet 0.
Answer: A E
Explanation
In this case, the following algorithm is used when multiple distribute-lists are used:
1. First check which interface is being sent out. If it is Ethernet 0, distribute-list 2 is applied first. If the network is denied then no further checking is done for this network. But if distribute-list 2 permits that network then distribute-list 1 is also checked. If both distribute-lists allow that network then it will be sent out.
2. If the interface is not Ethernet 0 then only distribute-list 1 is applied.
Now let’s take some examples.
+ If the advertised network is 10.0.1.0/24, it will be sent out all interfaces, including Ethernet 0.
+ If the advertised network is 10.0.2.0/24, it will be sent out all interfaces, excepting Ethernet 0.
+ If the advertised network is 11.0.0.0/8, it will be dropped.
Note: It is possible to define one interface-specific distribute-list per interface and one protocol-specific distribute-list for each process/autonomous-system.
(For more information, please read: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_tech_note09186a0080208748.shtml)
Question 6
Refer to the exhibit. Examine the partial configuration and the routing table excerpt. Which routes would be redistributed into OSPF area 1?
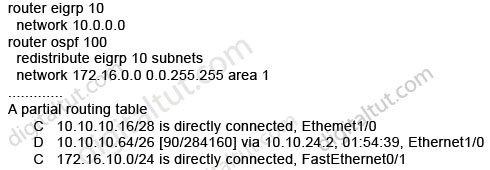
A. 10.10.10.16/28 only
B. 10.10.10.16/28 and 10.10.10.64/26
C. 10.10.10.16/28, 10.10.10.64/26, and 172.16.10.0/24
D. 10.10.10.64/26 only
Answer: B (but in the exam you should choose D)
Explanation
The network 172.16.10.0/24 belongs to OSPF (we know from the “network 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 1” command) so it will not be redistributed.
When using the “subnets” keyword, all the connected networks will be redistributed so 10.10.10.16/28 & 10.10.10.64/26 will be redistributed, too. You can read my GNS3 lab about this topic here: http://www.digitaltut.com/redistribute-eigrp-and-ospf-gns3-lab.
Therefore the correct answer should be B but in the exam you should choose D. Maybe it is a mistake of Cisco.
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. A partial routing configuration is shown. Complete the configuration so that only the default-network is redistributed from EIGRP 190 into EIGRP 212. Which ACL statement completes the configuration correctly?
| router eigrp 190 redistribute eigrp 212 network 192.0.0.0 0.0.0.3 ! router eigrp 212 redistribute eigrp 190 route-map default_route network 212.50.185.96 0.0.0.31 ! route-map defau1t_route permit 10 match ip address 100 |
A. access-list 100 permit ip 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
B. access-list 100 permit ip host 0.0.0.0 any
C. access-list 100 permit ip any host 0.0.0.0
D. A default-network cannot be redistributed between routing processes.
Answer: C
Explanation
The command “access-list 100 permit ip any host 0.0.0.0” means permit any source address with the destination of 0.0.0.0/0, which is the default route
Note:
any equals 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255
host 0.0.0.0 equals 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit. Router B and router C are performing mutual redistribution between OSPF and EIGRP, and their default metrics are configured the same. Router D has equal cost paths to networks where both paths are not really equal cost. For example, network 172.16.54.0 shows equal cost through both router B and router C, though in reality the cost is greater using router C. Other routers, though not shown, are connected to the 172.16.54.0 and 172.16.55.0 networks, and the same issues exist to those routers and the networks connected to them.
What can be done so that data will be routed along the most optimal path in the network?
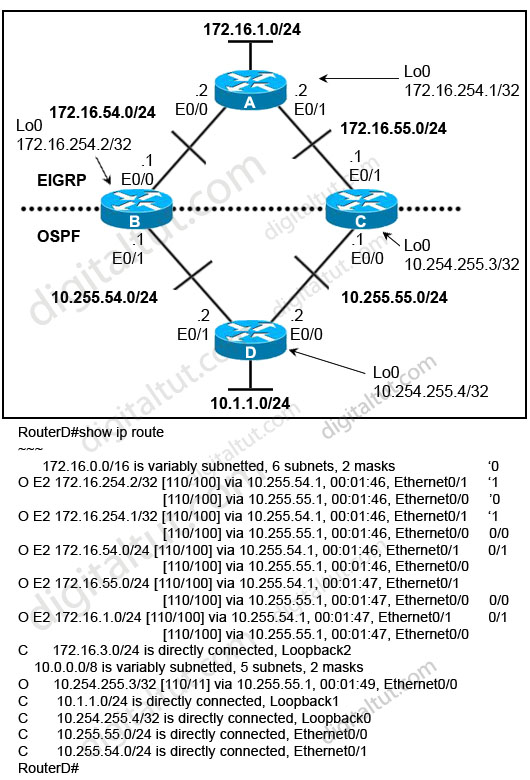
A. Redistribute connected interfaces on router B and router C.
B. Set the maximum number of equal cost paths to 1 in all routers.
C. When redistributing EIGRP into OSPF, set the external metric type to type E1.
D. Adjust the default metrics in router B and router C so that the values are different in each router.
E. None of these solutions will fix the problem. Migrate to a single dynamic routing protocol.
Answer: E
Explanation
Let’s discuss about answers C & D first.
From the output, we learn that all the External OSPF routes have metrics of 100 (the second parameters in [110/100]). This is not the default metric of OSPF Type 2 External route (the default value is 20) so the metrics of redistributed routes have been modified. Maybe when redistributing into OSPF, the “metric” in the “redistribute” command or the “default-metric” command was used on router B & C to assign the metric of these routes. Something like this:
| router ospf 1 redistribute eigrp 1 metric 100 subnets |
or
| router ospf 1 ….. default-metric 100 |
Therefore even if we use the metric type E1 the problem still exists because the link B-D & C-D seems to have the same metric -> the total metrics remains the same -> C is not correct.
We can use route-map and set different metrics for each networks but some unshown networks will have the same issues -> D is not a good choice
So the best answer should be E.
Question 9
Refer to the exhibit. A new TAC engineer comes to you for advice. The engineer wants to configure RIPv2-OSPF two-way redistribution while avoiding routing loops. Which two additions to the router B1 configuration should the engineer make? (Choose two)
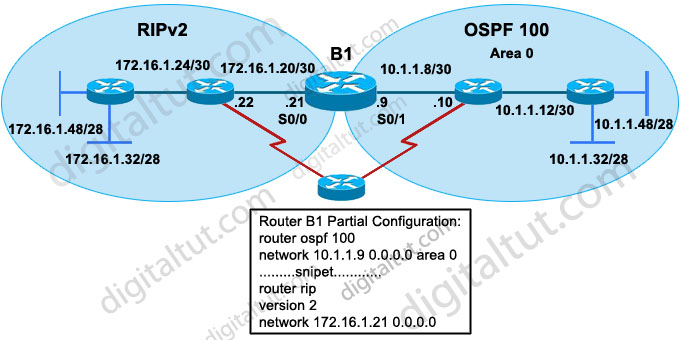
A. access-list 40 deny 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 40 permit any
router rip
redistribute ospf 100 metric 5
distribute-list 40 out ospf 100
B. ip prefix-list rip_routes permit 172.16.1.16/25 ge 26 le 28
route-map redis-ospf deny 10
match ip address prefix-list rip_routes
router rip
redistribute ospf 10 route-map redis-ospf subnets
C. ip prefix-list rip-to-ospf permit 10.1.1.8/25 ge 26 le 28
route-map redis-rip deny 20
match ip address prefix-list rip-to-ospf
router ospf 100
redistribute rip route-map redis-rip subnets
D. access-list 15 deny 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.63
access-list 15 permit any
route-map redis-rip deny 10
match ip address 15
route-map redis-rip permit 20
router ospf 100
redistribute rip route-map redis-rip subnets
Answer: A D
Explanation
B1 is not the only router that redistributes between RIP & OSPF. The “small” router below B1 can be configured for this task too so B1 can try to redistribute networks advertised by that “small” router again. Therefore it is necessary to filter out networks that have been advertised by the “small” router. For example, we need to prevent network 172.16.1.0/24 from advertised back into RIPv2 or network 10.1.1.0/26 from advertised back into OSPF. Notice that all networks in OSPF domain (including 10.1.1.8/30, 10.1.1.12/30, 10.1.1.48/28, 10.1.1.32/28) can be summarized as 10.1.1.0/26 and all networks in RIP domain (including 172.16.1.24/30, 172.16.1.20/30, 172.16.1.32/28, 172.16.1.48/28) can be summarized as 172.16.1.0/24 -> answers A & D are correct.
In answer B, the command “ip prefix-list rip_routes permit 172.16.1.16/25 ge 26 le 28” means:
+ First check the first 25 bits of the address -> this will allow addresses from 172.16.1.0 to 172.16.1.127

+ If those match then check the subnet mask, which in this case can be GREATER THAN or EQUAL to 26 bits & LESS THAN or EQUAL to 28 bits -> meaning that /26, /27, /28 subnet masks would match.
For example, networks 172.16.1.0/26; 172.16.1.16/28 would match (but notice networks 172.16.1.0/25; 172.16.1.128/26 wouldn’t).
In the “ip prefix-list rip_routes permit 172.16.1.16/25 ge 26 le 28”, the prefix-list “rip_routes” only covers networks 172.16.1.32/28 & 172.16.1.48/28 but can’t cover networks 172.16.1.24/30 & 172.16.1.20/30. Also, the OSPF process in the “redistribute” command should be 100, not 10 -> B is not correct.
Same problem as answer B, the prefix-list in answer C can’t cover networks 10.1.1.8/30 & 10.1.1.12/30 -> C is not correct.
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator is trying to configure mutual redistribution between EIGRP and OSPF. Autosummarization in EIGRP 100 AS is disabled. After adding OSPF configuration to router E31, the network administrator checked the routing table of router B2, but none of the EIGRP routes appeared there.
To redistribute the EIGRP AS 100 routes into OSPF, which command should be added, or edited, on router B1 under router ospf 10?
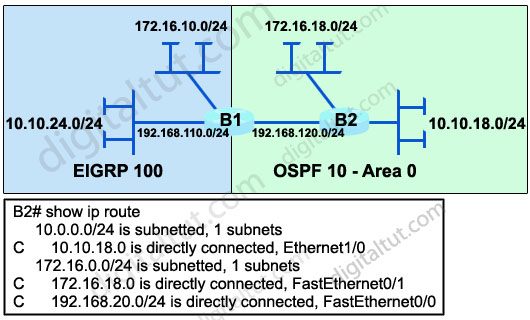
A. redistribute eigrp 100 metric-type 1
B. redistribute eigrp 100 subnets
C. no auto-summary 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
D. area 0 range 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0
Answer: B
Explanation
When redistributing into OSPF without keyword “subnets”, only classful networks will be redistributed. Classful networks here mean networks with the default major subnet masks (for example 10.0.0.0/8; 180.1.0.0/16; 200.200.200.0/24…).
In fact, the routing table on the exhibit above is not totally correct. The network 192.168.110.0/24 will be redistributed and shown in the routing table of B2 even if the keyword “subnets” is not used because it belongs to class C with the default subnet mask of class C.
To make all the networks, including subnets appear in the routing table of B2 we must use keyword “subnets” when redistributing into OSPF. This is also an important thing to remember when redistributing into OSPF.
Please read my Redistribute EIGRP and OSPF – GNS3 Lab if you are still not sure about this.
Question 11
Refer to the exhibit. Routers R1 and R2 are running EIGRP and have converged. On the basis of the information that is presented, which statement is true?
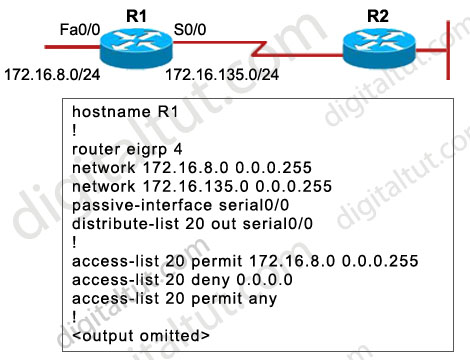
A. All outgoing routing updates from router R1 to router R2 will be suppressed, but the inbound updates will continue to be received.
B. All incoming routing updates from R2 will be suppressed, but the outgoing updates will continue to be sent.
C. Both outgoing and incoming routing updates on R1 will be stopped because of the passive-interface Serial0/0 configuration statement.
D. Both outgoing and incoming routing updates on R1 will be permitted because the distribute-list 20 out Serial0/0 command cannot be used with association with the outgoing interface.
Answer: C
Explanation
In EIGRP (and OSPF) the passive-interface command stops sending outgoing hello packets, hence the router can not form any neighbor relationship via the passive interface. This behavior stops both outgoing and incoming routing updates -> the distribute-list has no use here.












